3D Printing Process
3D Printing Process

3D Printing Process
The 3D printing process consists of three main steps. First, you need to obtain a printable 3D model. Then, you should prepare it for printing, and the last step is the printing job itself. Let’s take a look at everything from a general perspective. Then, we’ll go more into detail.
The first step is to obtain a 3D object, which is typically an STL file. However, this format is not recognized by 3D printers and it is not directly printable. To process an STL file, you need to use a specialized tool, commonly known as ‘slicer’. There are different slicers on the market, some are free (PrusaSlicer), others are paid (Simplify3D) and they are usually compatible with a limited range of printers, so you need to choose the right one for your machine. You can import an STL file into the slicer of your choice, configure printing parameters and then export the final result as a ‘G-code’, which is basically the original 3D object sliced into thin layers and converted into a set of movement commands recognized by 3D printers. Furthermore, slicers insert additional information into G-codes, such as temperature information, cooling settings and others. The resulting G-code is printer-specific, so that’s why 3D objects are usually shared as STL files – users can then slice them for their printer / filament individually.
The diagram below depicts the individual steps leading towards a successful 3D print.
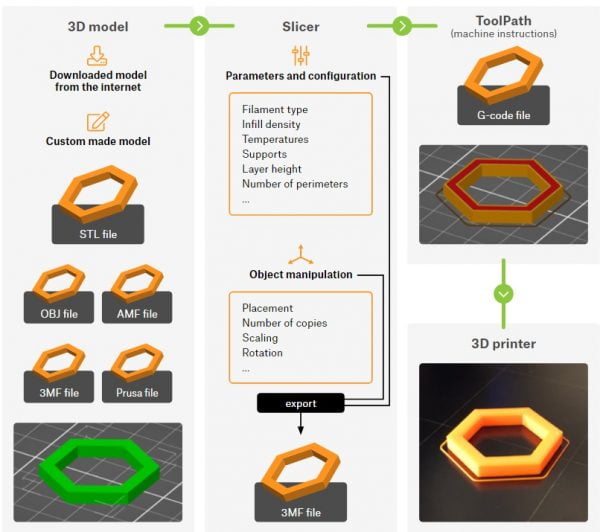
Getting a 3D model
Generally speaking, a 3D model can be obtained through one of the following ways:
- Downloading a 3D model from the internet
- Creating your own models
- 3D scanning a real-world object
Online libraries and 3D hubs
The easiest way how to get started with 3D printing is to find 3D objects available on the internet for free. They usually come in .stl or .obj file formats. There’s a number of websites that offer a wide range of downloadable models
Thingiverse – Thingiverse is the richest 3D archive on the internet. Currently, it offers more than 1.2 million models for free download – and the number keeps growing every day. It became a popular place for downloading, sharing and showcasing all sorts of 3D models.
YouMagine – YouMagine is a community website backed by Ultimaker. Models are divided into popular categories or collections curated by the site’s users. As of right now, the portal offers over 15,000 models for download.
PinShape – According to the creators, Pinshape is a shop with high-quality 3D models. However, the website also offers many models for free. Designers can use this web to sell their own creations.
MyMiniFactory – A popular repository with around 50,000 models by professional designers. All models are tested before publishing, so you can be sure you’re getting great quality STLs. The price of paid models is usually between 4 to 40 USD.
Cults3D – A repository with more than 25,000 free 3D models and several thousands of paid models. An interesting difference between this site and the rest are various collections based around popular brands, such as Lego, IKEA or GoPro.
3D modeling software
Nowadays, you can pick from a wide range of various 3D modeling applications. There are simple and easy-to-learn (and often web-based) applications such as TinkerCad. You can try parametric modeling with OpenSCAD, or use a fully professional tool such as the popular Autodesk Fusion 360. All these applications enable you to create a model and export it as an STL file.
OpenSCAD
OpenSCAD is an open-source project available for free from OpenSCAD – It takes a completely different approach to 3D modeling – everything is done by writing code. The user interface is divided into two parts. In the left section, the user defines 3D objects by ‘programming’ them, while in the right section, a 3D preview is displayed. The application works mostly with a couple of primitives (cube, cylinder, sphere,…) and basic boolean operations (join, cut, intersection). However, the program also allows for advanced scripting – you can use commonly known operators, such as if, while, for, logical operators and others. If you feel you are more of a programmer than an artist, you may give OpenSCAD a go.
Tinkercad
Tinkercad is a great and intuitive tool for beginners. It’s free, although a registration is required. You can find plenty of tutorials, guides and tips online. TinkerCad is built around the idea of a basic library with various shapes, which can be dragged into the main window and further modified. The application lacks advanced functions, however, it can import and edit an existing STL file.
Autodesk Fusion 360
If you want to start designing more complex objects, or even various components that should fit together, then you need to select a more professional tool. Fusion 360 is a popular option. Users can work in both CAD (Computer-aided Design) and CAM (Computer-aided Manufacturing), strength analysis or visualizations. Fusion 360 offers not only parametric modelling, but even sculpting as well. Let’s take a look at these two methods more closely. Fusion 360 is becoming more and more popular also thanks of the fact it’s free to use for makers, innovators, enthusiasts and small companies with a turnover of up to 100,000 USD a year. If this program caught your attention, go right ahead – it’s a great tool with an active community around it. Plus, you can find tons of tutorials online.
Parametric modeling
Parametric modeling is a common way of creating structural models or mechanical parts. The object starts as a 2D shape using basic primitives (such as a line, square, rectangle, point…). Next, the object is extruded, which turns it into a 3D shape. Now, imagine that we want to create a model of a dog. Using parametric modeling is inefficient and too complicated, because we want to create an organic shape. This is where sculpting steps in. Digital sculpting is somewhat similar to real-world sculpting (e.g. using a sculpey or similar material), however it has many advantages – such as the undo function. The primitive objects in this case are already 3D objects – cube, sphere, cylinder, toroid and others. These objects can be freely extruded, squished, bent.
Blender
Blender is probably the best free 3D modeling tool available today. It’s developed under an open-source license and it’s available for Windows, Mac and Linux. It may be a bit too complex for a beginner, chaotic even. However, it has found its way into the hearts of many users. Especially users with artistic ambitions, who don’t need precise parametric modeling, found Blender to be an amazing tool. Sculpting, texturing, animations… Blender is a Swiss army knife among 3D modeling applications.
You can also try the following applications
Microsoft 3D Builder
Meshmixer
Rhinoceros3D
FreeCAD
AutodeskInventor
SolidWorks
Autodesk AutoCAD
SketchUp